Legal Framework for FEED in Vietnam: A Key Milestone Begins with Key Railway Projects
On 11 June 2025, the Government of Vietnam issued Decree 123/2025/ND-CP detailing FEED applying for key railway projects as follows:
- Lao Cai – Ha Noi – Hai Phong Line
- North – South Express Railway
- Metro Systems in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City
Download PDF file Here
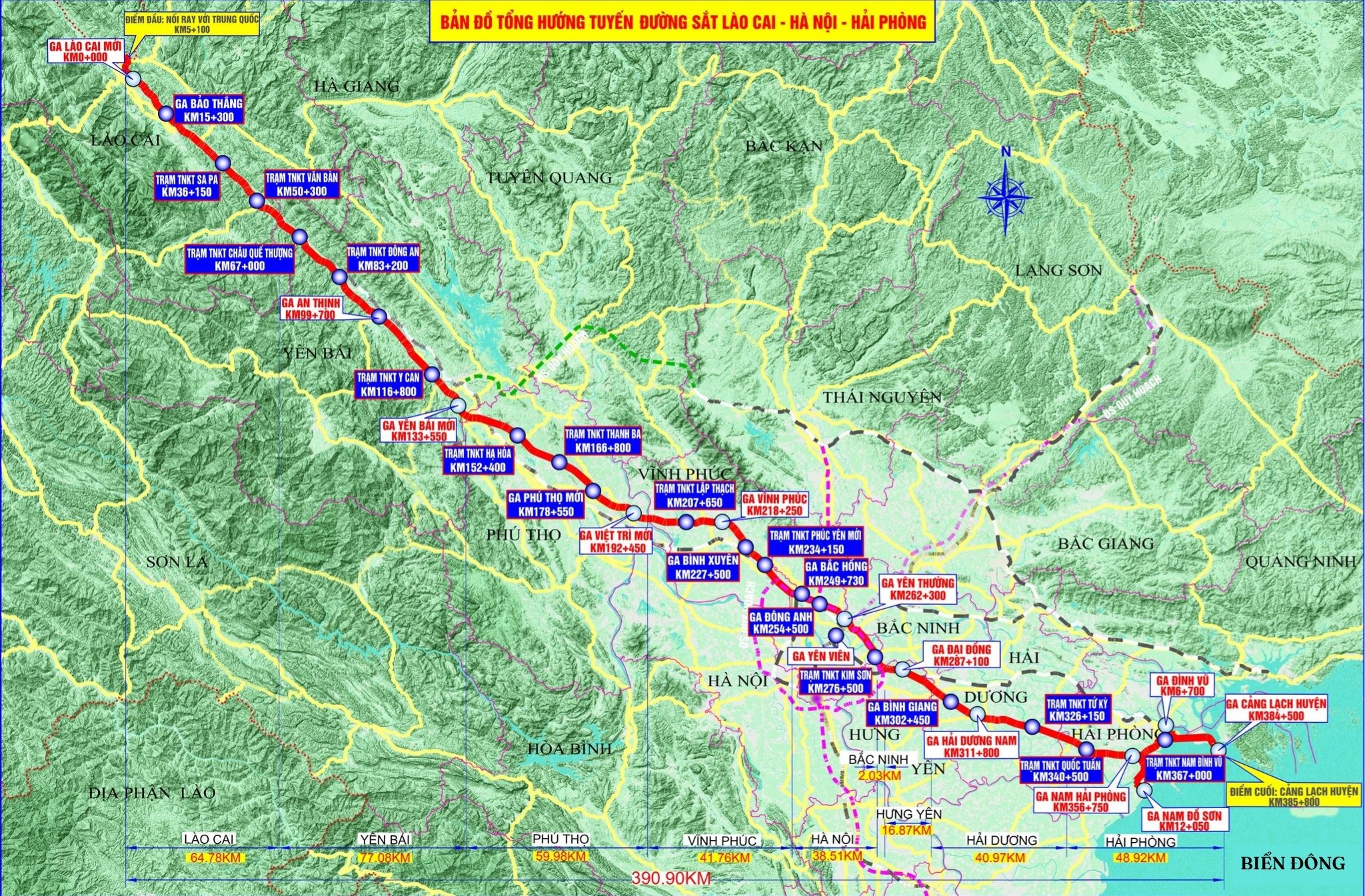
Lao Cai – Ha Noi – Hai Phong Line
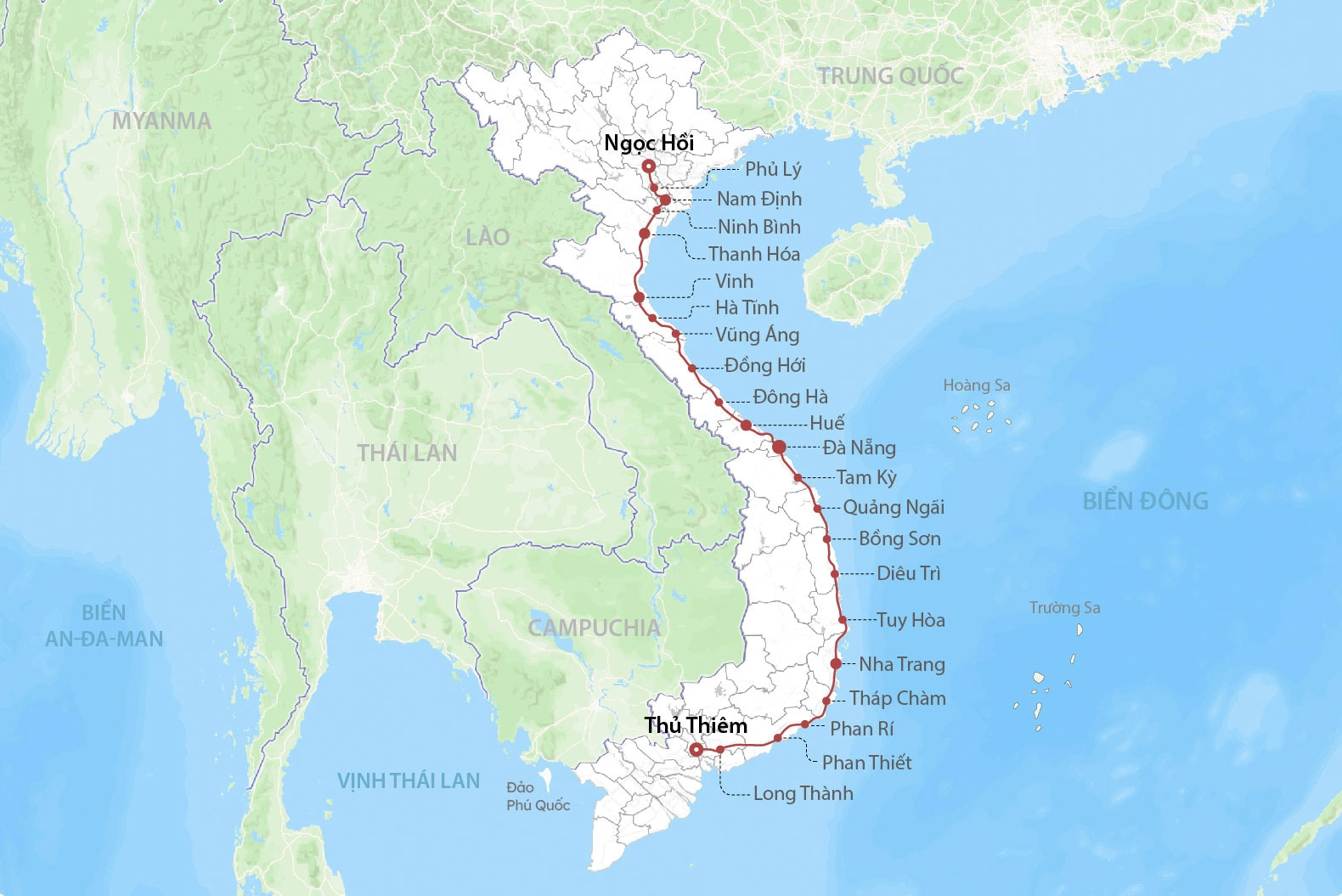
North – South Express Railway
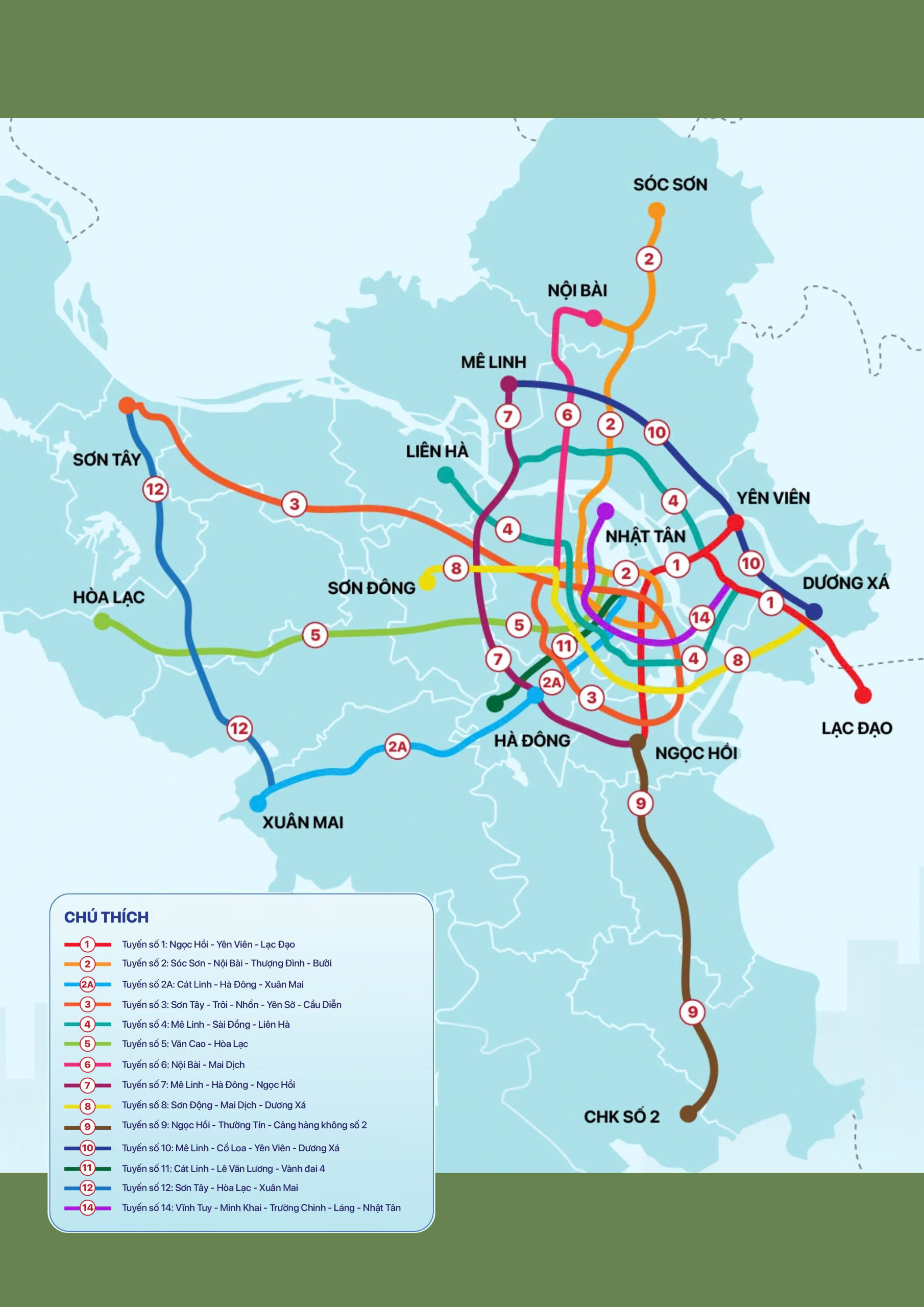
Metro systems in Hanoi
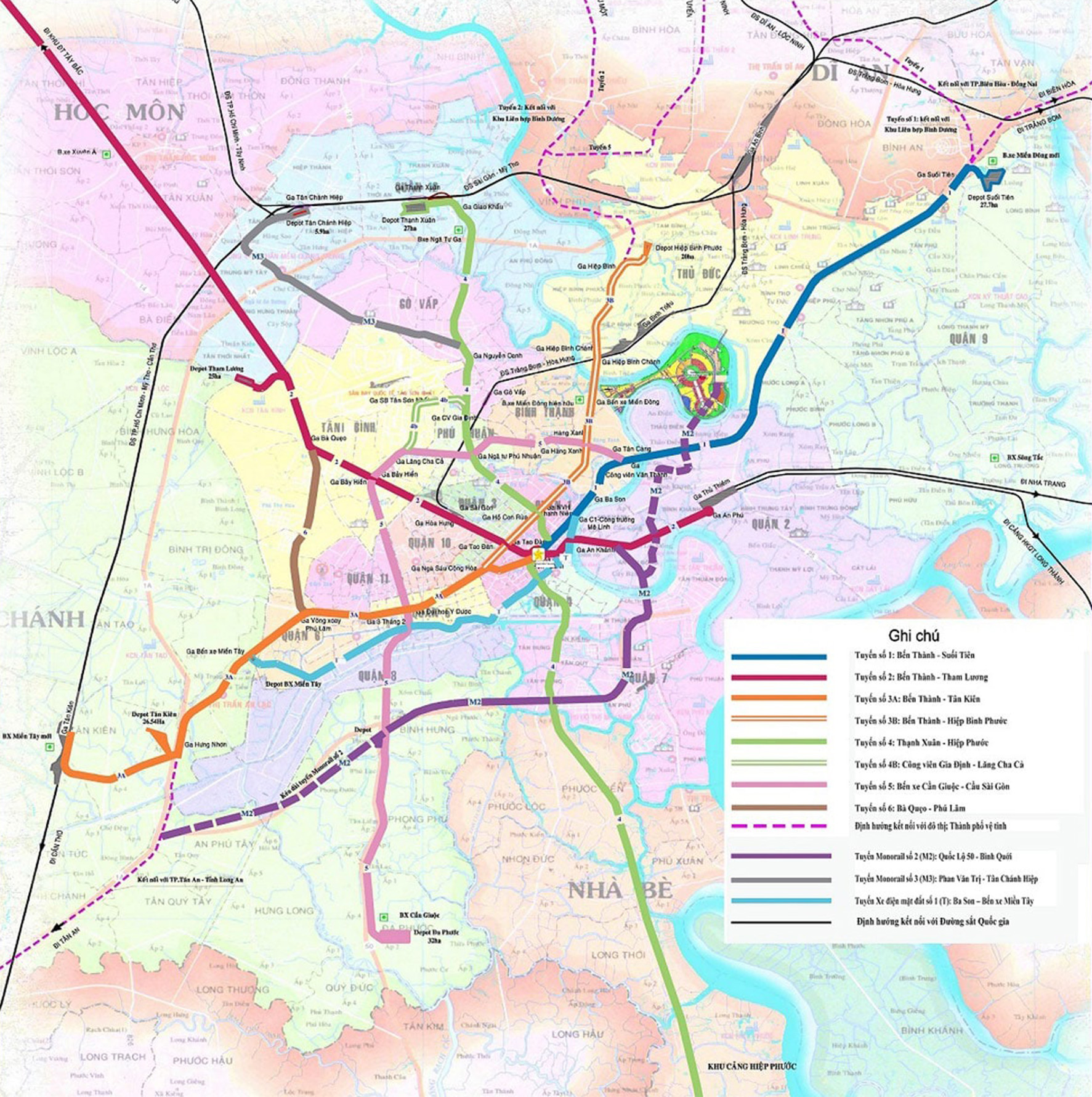
Metro systmes in Ho Chi Minh City
With Decree 123/2025, Vietnam is moving closer to international construction practices, since FEED is widely used in significant infrastructure projects worldwide (such as express railways, metro systems, seaports, airports).
This event is expected to enhance key infrastructure projects in Vietnam, particularly PPP projects and ODA-funded projects supported by loans from ADB, WB or JICA.
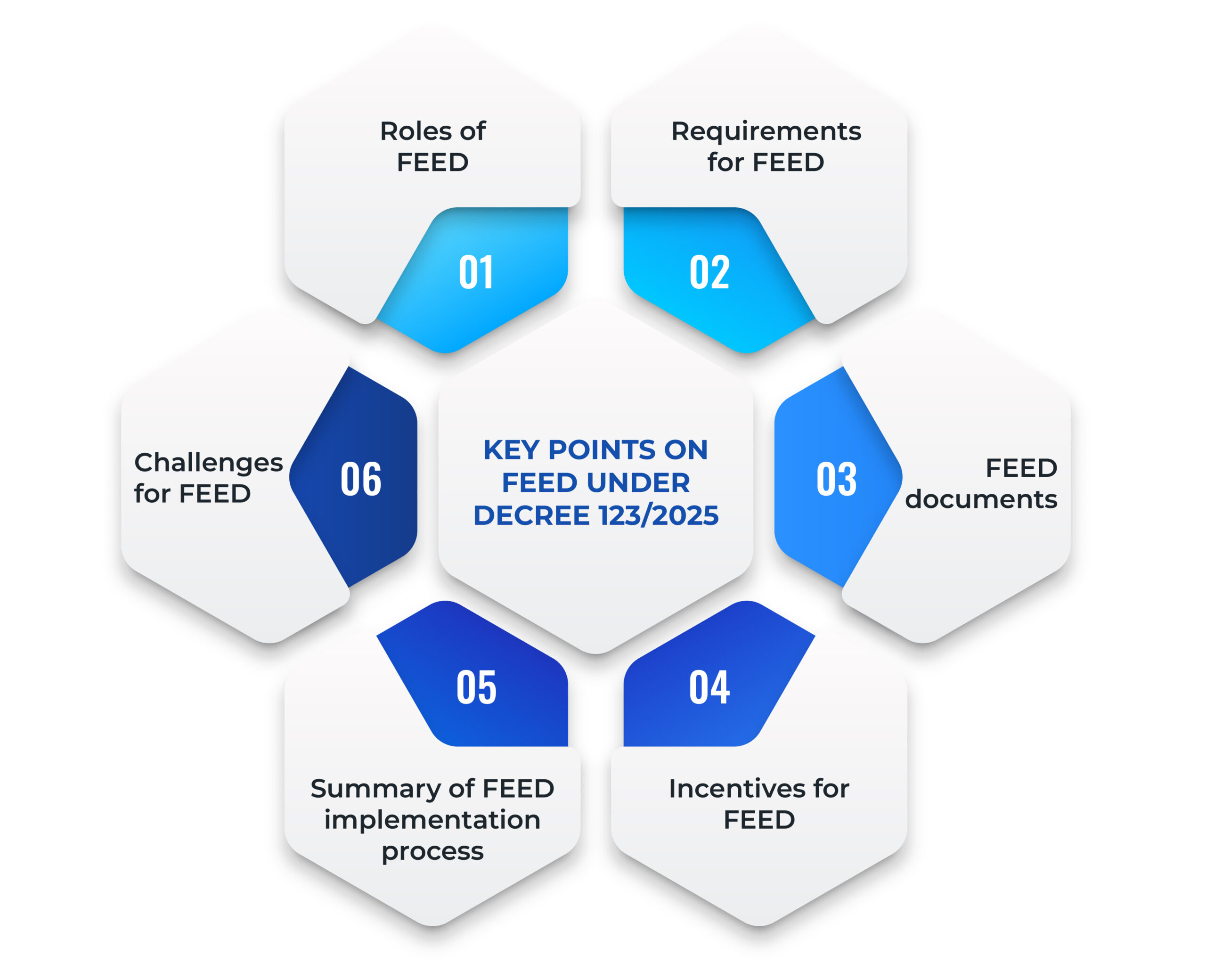
Under this Legal Update, CNC will outline the key points on FEED as governed by Decree 123/2025, including:
- Roles of FEED
- Requirements for FEED
- FEED documents
- Incentives for FEED
- Summary of FEED implementation process
- Challenges for FEED
Key points on FEED under Decree 123/2025
Roles of FEED
In key railway projects, the FEED (Front-End Engineering Design) may substitute the basic design in the Feasibility Study Report for Construction Investment. Accordingly, there are 02 design phases in such projects: (i) the FEED and (ii) the post-FEED (detailed design/shop drawings).[1]
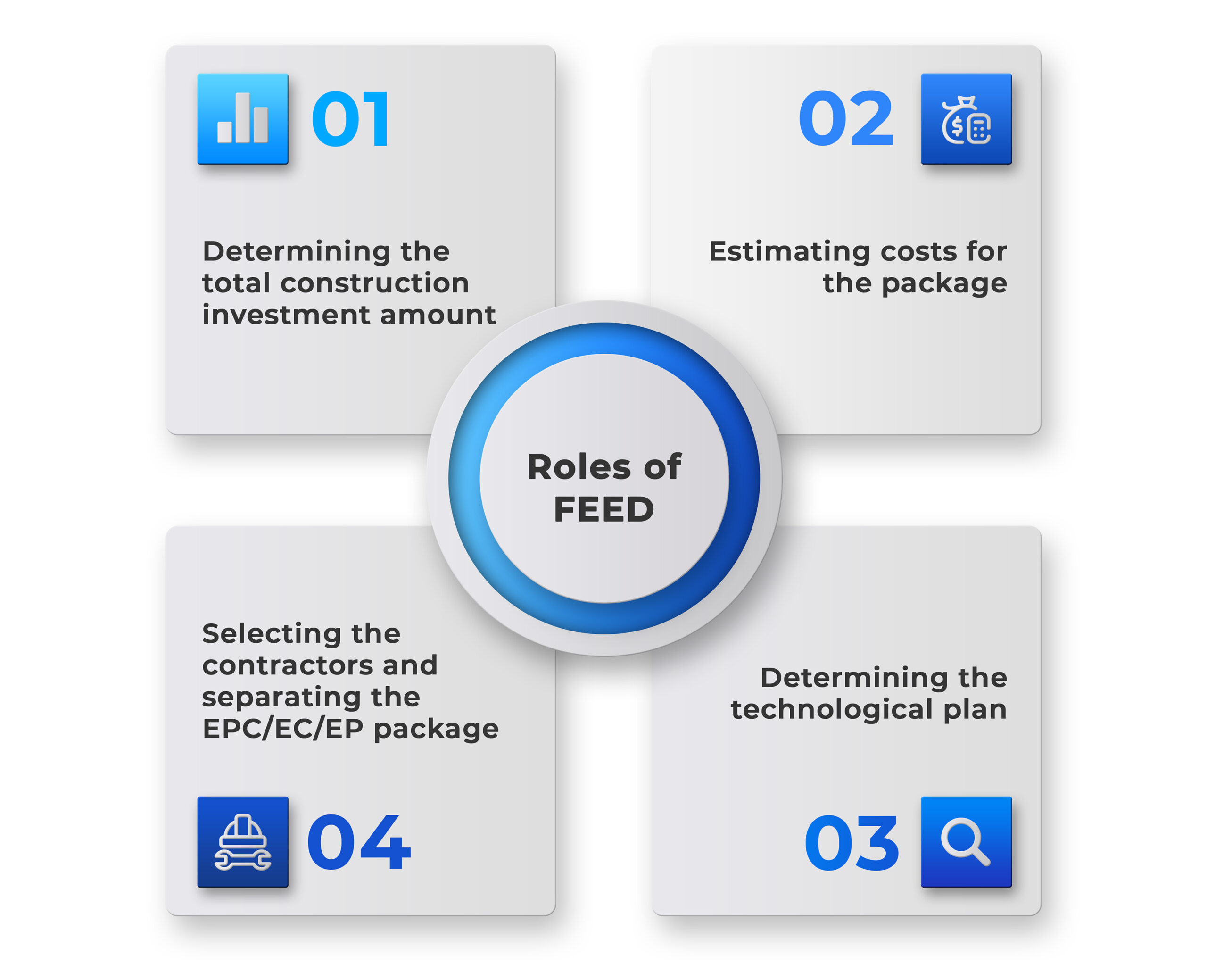
The FEED shall detail the requirements on technology and technique, and such detailed information shall serve as the basis for implementing the subsequent works such as:[2]
- Determining the total construction investment amount
- Estimating costs for the package
- Determining the technological plan
- Selecting the contractors and separating the EPC/EC/EP package in the FEED phase
Roles of FEED
With these merits, the FEED becomes a tool that enhances transparency and detail, while minimizing the risks of increased capitals and delays – a long-standing issue in key projects of Vietnam.
On the contrary, such merits are not found in the basic design, as it only includes the preliminary technical direction and reference, with a low level of technical detail.
Requirements for FEED
There are several requirements for FEED such as:[3]
- Complying with the design mission and investment policy
- Complying with the applied standards and requirements on safety, environment, fire prevention and fighting
- Feasibility and effectiveness provided by the design solution
- Full contents on the overall structure of the system and information/parameters/dimensions/materials
- Attaching BIM which includes an appropriate level of information in the original and open form
- Regulations on FEED documents (see details below)

Requirements for FEED
FEED documents
FEED documents shall include:[4]
- Design information
- Design drawings including names, signatures and seals of (i) designer, (ii) design reviewer, (iii) design lead, (iv) design manager, (v) project-forming consultant, (vi) FEED-forming consultant.
- Specifications
- Other related documents
Furthermore, FEED documents shall be preserved for the long term.

Parties whose names, signatures and seals in the FEED
Incentives for FEED
Decree 123/2025 provides several special policies for FEED, such as:
- Encouraging the application of new technologies: Digital Twin, GIS, AIM[5]
- Employing the foreign consultant for FEED and related works[6]
- Conducting the steps in the preparation stage concurrently to accelerate progress[7]
Summary of FEED implementation process
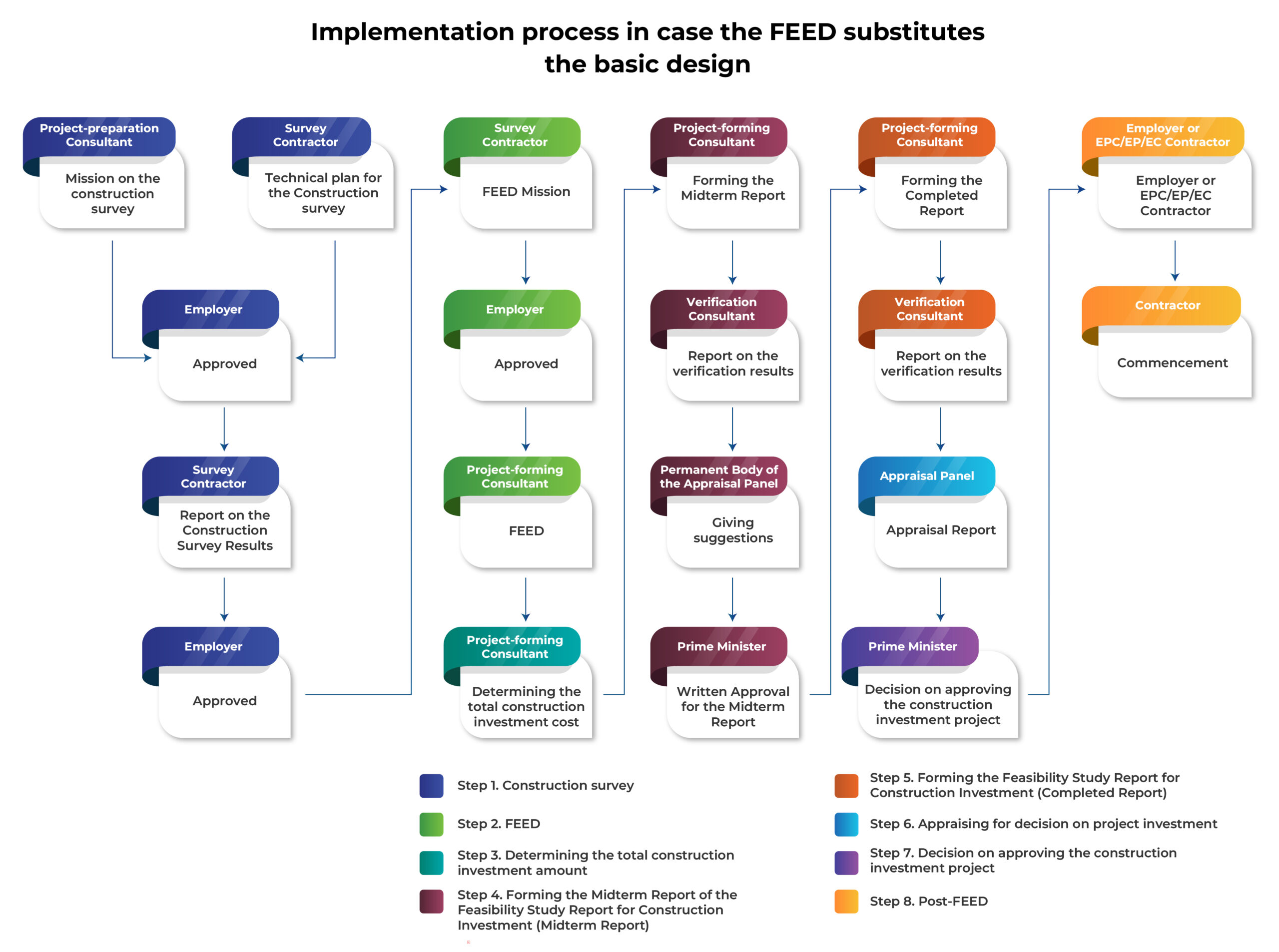
The FEED implementation process shall be considered the most noteworthy point in Decree 123/2025. Accordingly, this process shall include 07 steps as follows:
- Construction survey
- FEED
- Determining the total construction investment amount
- Forming the Midterm Report of the Feasibility Study Report for Construction Investment (Midterm Report)
- Forming the Feasibility Study Report for Construction Investment (Completed Report)
- Appraising for decision on project investment
- Decision on approving the construction investment project
- Post-FEED
To facilitate tracking the FEED implementation process, CNC will share the following flowchart:
Step 1. Construction Survey
The Employer shall approve the mission on the construction survey (formed by the project-preparation consultant) and technical plan for the construction survey (formed by the survey contractor).[8]
Based on the approved mission and technical plan for the survey, the survey contractor shall conduct the survey and prepare the Report on the Construction Survey Results. Subsequently, the survey contractor shall submit this Report to the Employer for approval.[9]
The Report on the Construction Survey Results shall serve as the basis for preparing FEED, the Midterm Report and the Completed Report. This Report is also a part of the work completion documents.[10]
Step 2. FEED
The FEED Mission shall serve as the basis for preparing FEED in the Feasibility Study Report for Construction Investment (including the Midterm Report and the Completed Report). Accordingly, the project-preparation consultant shall prepare this Mission and submit it to the Employer for approval.[11]
Subsequently, the FEED shall be implemented based on the approved FEED Mission. Additionally, the FEED shall comply with the regulations on FEED documents as outlined above.
Step 3. Determining the total construction investment amount
Based on the FEED, the project-forming consultant shall determine the total construction investment amount, which includes the estimated costs for completing the Midterm Report, and the total amount for completing the Completed Report.[12]
Generally, the total construction investment amount shall comprise:
- Costs of compensation, support and resettlement
- Construction costs
- Equipment costs
- Project management costs
- Investment consulting costs
- Contingency costs
- Other costs
Step 4. Forming the Midterm Report
Under the approved FEED design mission, the project-forming consulant shall prepare the Midterm Report.[13]
The Midterm Report shall include:[14]
- General information on the project
- Analysis of the technical plan, line plan, position on the main work
- The estimated total construction investment amount
- Preliminary assessment on the economic effectiveness, rate of progress and risks
- Suggestions on the optimal plan
- Suggestions on the project separation
- The preliminary FEED documents
Concurrently, the Prime Minister shall establish a State Appraisal Panel.[15] This Panel shall select the Verification Consultant to prepare the Report on the Verification Results for the Midterm Report.[16]
Based on the Report on the Verification Results and the suggestions from the Permanent Body of the Appraisal Panel, the Prime Minister issues the Written Approval for the Midterm Report. This Approval shall serve as the basis for preparing the Completed Report.[17]
Step 5. Forming the Completed Report
Following the approval of the Prime Minister on the Midterm Report, the project-forming consultant shall complete the Completed Report for appraisal and decision on the project investment. The Completed Report shall include:[18]
- General explanation (including the total construction investment amount)
- The completed FEED documents
- The completed design for fire prevention and fighting
- Documents related to suggestions on the conversion of the forest using purpose
- Documents related to the general plan for contractor selection, the plan on package separation and the estimated costs of EPC/EC/EP packages
- Other related documents
The Verification Consultant formed the Report on the Verification Results for the Completed Report.[19]
Step 6. Appraising for decision on project investment
The Employer submits the documents collected in Step 4 and Step 5 to the Prime Minister and the Appraisal Panel.[20]
The Appraisal Panel issues the Appraisal Report within 30 days of receiving the valid documents from the Employer.[21]
Step 7. Decision on approving the construction investment project
Based on the Appraisal Report of the Appraisal Panel and the audit results on the total construction investment amount of the State Audit, the Prime Minister shall consider issuing the Decision on approving the construction investment project.[22]
Step 8. Post-FEED
The Employer or EPC/EC/EP Contractor shall form and approve the post-FEED. This design shall be the basis for construction.[23]
Challenges for FEED
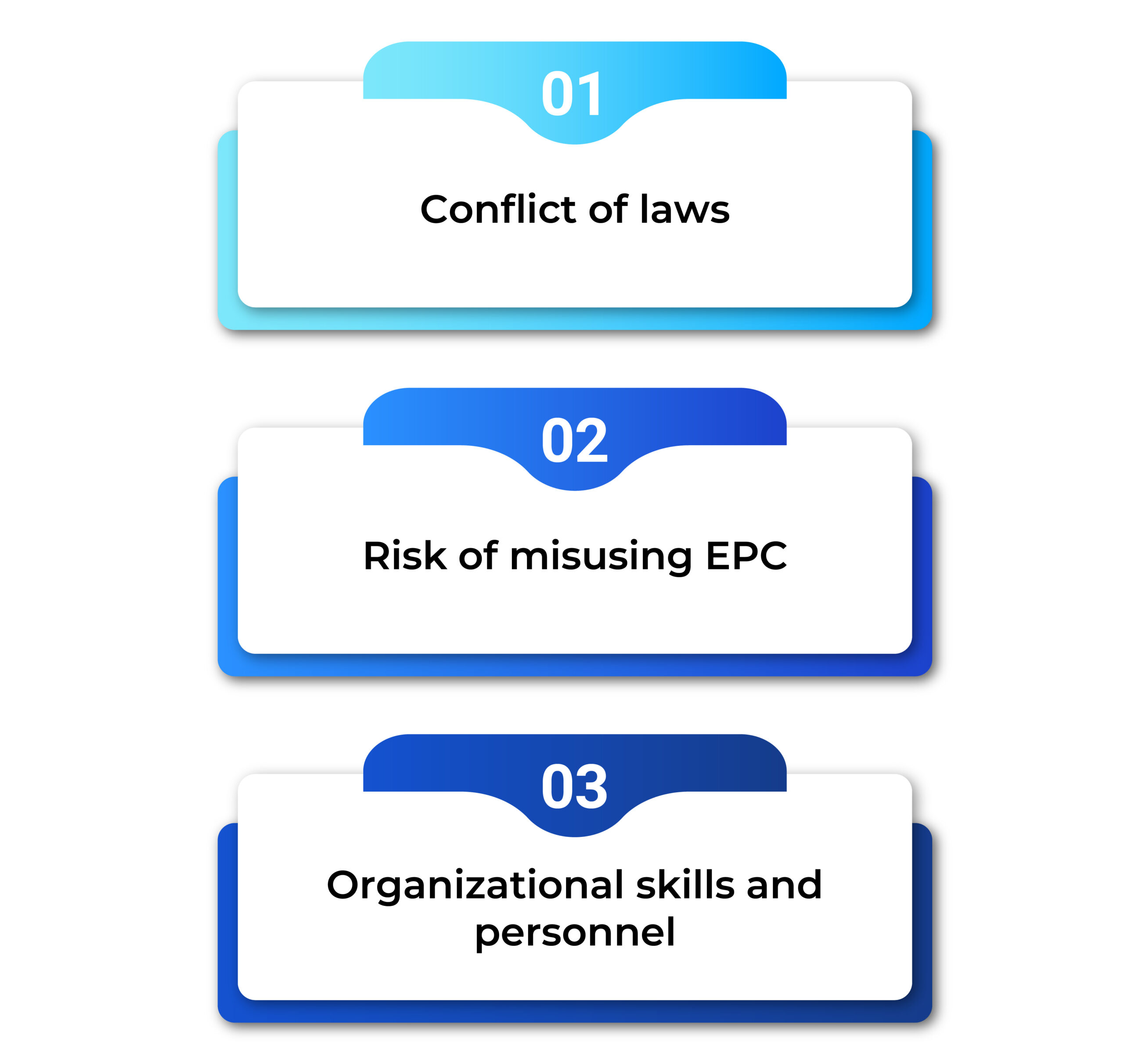
There are several challenges for FEED during the implementation of key railway projects.
The first challenge is the conflict of laws. Accordingly, Decree 123/2025 overlaps with many provisions in the current Law on Construction. For instance, the Law on Construction requires the inclusion of the basic design in the Feasibility Study Report for Construction Investment, and it does not recognize FEED as a valid design phase.
The second is the risk of misusing EPC during the project implementation. Accordingly, Decree 123/2025 permits the selection of EPC Contractors during the FEED phase. However, in case the EPC Contractor lacks the skills to review FEED documents, he/she may prepare the FEED in a way that favors himself/herself, leading to the Employer becoming more dependent on a non-optimal FEED.
The third is related to organizational skills and personnel, since most domestic consultants are not familiar with FEED, and lack the experience with BIM and other new technological applications. Moreover, there are concerns about the ability of the administrative authorities to appraise the documents that are more complicated than the basic design.
Challenges for FEED
Written by
 |
Senior Associate I Tran Pham Hoang Tung
Phone: (84) 901 334 192 Email: tung.tran@cnccounsel.com |
 |
Legal Assistant I Pham Nguyen Tan Trung
Phone: (84) 028 6276 9900 Email: trung.pham@cnccounsel.com |
[1] Article 3.1 & 4.4 Decree 123/2025
[2] Article 10.4, 13.1(d) & 13.5 Decree 123/2025
[3] Article 10 Decree 123/2025
[4] Article 10.6 Decree 123/2025
[5] Article 4.3 Decree 123/2025
[6] Article 4.7 Decree 123/2025
[7] Article 4.5 Decree 123/2025
[8] Article 6.1 & 6.5 Decree 123/2025
[9] Article 7 & 8.1 Decree 123/2025
[10] Article 7.1, 7.4 & 8.3 Decree 123/2025
[11] Article 9.1 Decree 123/2025
[12] Article 22 &23 Decree 123/2025
[13] Article 11.1 Decree 123/2025
[14] Article 12 Decree 123/2025
[15] Article 14.1 Decree 123/2025
[16] Article 15 Decree 123/2025
[17] Article 11.3 &16 Decree 123/2025
[18] Article 13 Decree 123/2025
[19] Article 15 Decree 123/2025
[20] Article 17.1 &17.2 Decree 123/2025
[21] Article 17.3 Decree 123/2025
[22] Article 17.4, 17.5 & 19.1 Decree 123/2025
[23] Article 21 Decree 123/2025




